Stylomastoid foramen
| Stylomastoid foramen | |
|---|---|
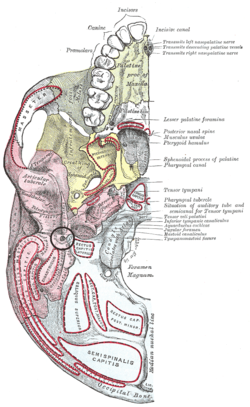 Base of skull. Inferior surface. Pink region is temporal bone, and stylomastoid foramen is in black circle at center of pink region. | |
 Left temporal bone. Inferior surface. (Stylomastoid foramen is third label from the bottom on the left.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Temporal bone of skull |
| System | Skeletal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen stylomastoideum |
| TA98 | A02.1.06.048 |
| TA2 | 684 |
| FMA | 55816 |
| Anatomical terms of bone [edit on Wikidata] | |
The stylomastoid foramen is a foramen between the styloid and mastoid processes of the temporal bone of the skull. It is the termination of the facial canal, and transmits the facial nerve, and stylomastoid artery. Facial nerve inflammation in the stylomastoid foramen may cause Bell's palsy.
Structure
The stylomastoid foramen is between the styloid and mastoid processes of the temporal bone. The average distance between the opening of the stylomastoid foramen and the styloid process is around 0.7 mm or 0.8 mm in adults, but may decrease to around 0.2 mm during aging.[1]
The stylomastoid foramen transmits the facial nerve,[2][3] and the stylomastoid artery.[3] These 2 structures lie directly next to each other.[3]
Clinical significance
Bell's palsy can result from inflammation of the facial nerve where it leaves the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. Patients with Bell's palsy appear with facial drooping on the affected side.
Additional images
-
 Facial canal
Facial canal - Lateral head anatomy detail. Facial nerve dissection.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 144 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 144 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Krmpotić Nemanić, Jelena; Vinter, Ivan; Ehrenfreund, Tin; Marušić, Ana (2008-12-17). "Postnatal changes in the styloid process, vagina processus styloidei, and stylomastoid foramen in relation to the function of muscles originating from the styloid process". Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. 31 (5): 343. doi:10.1007/s00276-008-0450-2. ISSN 1279-8517.
- ^ Curtin, H D; Wolfe, P; Snyderman, N (October 1983). "The facial nerve between the stylomastoid foramen and the parotid: computed tomographic imaging". Radiology. 149 (1): 165–169. doi:10.1148/radiology.149.1.6611924. ISSN 0033-8419.
- ^ a b c Bourdon, Nicolas; Babin, Emmanuel; Moreau, Sylvain; Salame, Ephrem; Valdazo, André; De Rugy, Marc Goullet; Delmas, Pierre (2000-09-01). "Facial Nerve: Vascular-Related Anatomy at the Stylomastoid Foramen". Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology. 109 (9): 849–852. doi:10.1177/000348940010900912. ISSN 0003-4894.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 22:4a-07 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy photo:22:os-0708 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon – illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (midearcavity)
- Diagram at patientsforum.com
- v
- t
- e
| Squamous part | |
|---|---|
| Lateral parts | |
| Basilar part |
|
| Other |
| Squamous part |
|
|---|---|
| Orbital part |
| Squamous part | |
|---|---|
| Mastoid part | |
| Petrous part |
|
| Tympanic part |
| Surfaces |
|
|---|---|
| Great wings | |
| Small wings | |
| Pterygoid processes | |
| Other |
| Plates | |
|---|---|
| Surfaces |
|
| Labyrinth |
|











