Reinecke's salt
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name ammonium (OC-6-11)-diamminetetrakis(thiocyanato-N)chromate(1−) | |
| Other names ammonium tetrathiocyanato- diamminechromate(III), Reinecke salt, | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.625 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C4H12N7OCrS4 |
| Molar mass | 354.42 g/mol |
| Appearance | dark red solid |
| Density | 1.49 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 270 °C (518 °F; 543 K) |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
Solubility in water | soluble in hot water |
| Structure | |
Coordination geometry | octahedral |
Dipole moment | 0 D |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards | toxic |
| GHS labelling: | |
Pictograms |   |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H332, H410 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P312, P322, P330, P363, P391, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | [Co(NH3)6]Cl3, KSCN, Chromium(III) chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
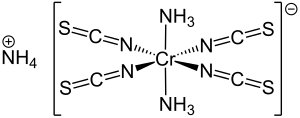
Reinecke's salt is an inorganic compound with the formula NH4[Cr(NCS)4(NH3)2]·H2O. The dark-red crystalline compound is soluble in boiling water, acetone, and ethanol.[2] It can be classified as a metal isothiocyanate complex.
Structure, preparation, reactions
The chromium atom is surrounded by six nitrogen atoms in an octahedral geometry. The NH3 ligands are mutually trans and the Cr–NCS groups are linear. The salt crystallizes with one molecule of water.[1]
It was first reported in 1863.[3] NH4[Cr(NCS)4(NH3)2] is prepared by treatment of molten NH4SCN (melting point around 145–150 °C) with (NH4)2Cr2O7.[4]
This salt was once widely used to precipitate primary and secondary amines as their ammonium salts. Included in the amines that effectively form crystalline precipitates are those derived from the amino acids, including proline and hydroxyproline. It also reacts with Hg2+ compounds, giving a red color or a red precipitate.
References
- ^ a b Saito, Y.; Takeuchi, Y.; Pepinsky, R. (1955). "The Crystal Structure of Ammonium Reineckate". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie, Kristallgeometrie, Kristallphysik, Kristallchemie. 106 (1–6): 476–477. doi:10.1524/zkri.1954.106.16.476. S2CID 101134761.
- ^ Peppel, T.; Schmidt, C.; Köckerling, M. (2011). "Synthesis, Properties, and Structures of Salts with the Reineckate Anion, [CrIII(NCS)4(NH3)2]−, and Large Organic Cations". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 637 (10): 1314–1321. doi:10.1002/zaac.201100091.
- ^ Reinecke, A. (1863). "Über Rhodanchromammonium-Verbindungen". Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie. 126: 113–118. doi:10.1002/jlac.18631260116.
- ^ Dakin, H. D. (1935). "Reinecke Salt". Organic Syntheses. 15: 74. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.015.0074.











