| WHRN |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1UEZ, 1UF1, 1UFX |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | WHRN, CIP98, PDZD7B, USH2D, WI, DFNB31, whirlin, Whirin |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 607928; MGI: 2682003; HomoloGene: 18739; GeneCards: WHRN; OMA:WHRN - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 9 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 9q32 | Start | 114,402,080 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 114,505,473 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 4 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 4 B3|4 33.97 cM | Start | 63,333,147 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 63,414,228 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - right adrenal cortex
- left adrenal gland
- left adrenal cortex
- left testis
- right testis
- pituitary gland
- right uterine tube
- anterior pituitary
- C1 segment
- body of uterus
|
| | Top expressed in | - neural layer of retina
- lumbar subsegment of spinal cord
- interventricular septum
- visual cortex
- primary visual cortex
- tail of embryo
- thymus
- superior frontal gyrus
- cerebellar cortex
- Rostral migratory stream
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
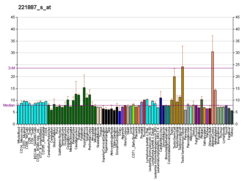 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- protein homodimerization activity
- protein heterodimerization activity
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- growth cone
- cell projection
- stereocilium
- photoreceptor inner segment
- stereocilia ankle link
- stereocilia ankle link complex
- actin filament
- cilium
- photoreceptor connecting cilium
- stereocilium bundle
- stereocilium tip
- ciliary basal body
- periciliary membrane compartment
- USH2 complex
- plasma membrane
- neuronal cell body
- cell junction
- synapse
| | Biological process | - retina homeostasis
- sensory perception of light stimulus
- hearing
- inner ear receptor cell stereocilium organization
- positive regulation of gene expression
- cerebellar Purkinje cell layer formation
- establishment of protein localization
- auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization
- paranodal junction maintenance
- detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001083885
NM_001173425
NM_015404
NM_001346890 |
| NM_001008791
NM_001008792
NM_001008793
NM_001008794
NM_001008795
|
|---|
NM_001008796
NM_001008797
NM_001008798
NM_001276371
NM_028640 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001077354
NP_001166896
NP_001333819
NP_056219 |
| |
|---|
NP_001008791
NP_001008792
NP_001008793
NP_001263300
NP_082916 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 9: 114.4 – 114.51 Mb | Chr 4: 63.33 – 63.41 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

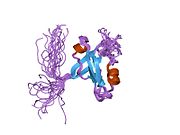 1uez: Solution structure of the first PDZ domain of human KIAA1526 protein
1uez: Solution structure of the first PDZ domain of human KIAA1526 protein 1uf1: Solution structure of the second PDZ domain of human KIAA1526 protein
1uf1: Solution structure of the second PDZ domain of human KIAA1526 protein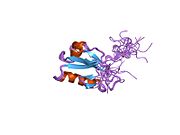 1ufx: Solution structure of the third PDZ domain of human KIAA1526 protein
1ufx: Solution structure of the third PDZ domain of human KIAA1526 protein





















